Key takeaways
- Open source test management tools cost less than commercial solutions. In 2025, 96% of organizations maintain or increase their open source adoption.
- Open source test management tools have some gaps. User interfaces aren’t as polished. Support is less predictable. Enterprise security features and advanced analytics are weaker.s.
- The total cost includes infrastructure, maintenance, integration work, and internal support. It goes beyond the free software.
- Kiwi TCMS is a strong competitor with a modern UI, active support, and solid features. It has API support, multiple user roles, and integration with popular bug trackers.
- TestLink provides reliable core functions with lots of community resources. The interface looks dated next to newer alternatives.
It’s never easy to make a decision on the right open source test management tool for your team. After all, this software should fit specific needs and the existing tech rather than just a new tech stack entry. Discover if any of the 13 top open source test management options might be great for your testing workflow 👇
What are Open Source Test Management Tools?
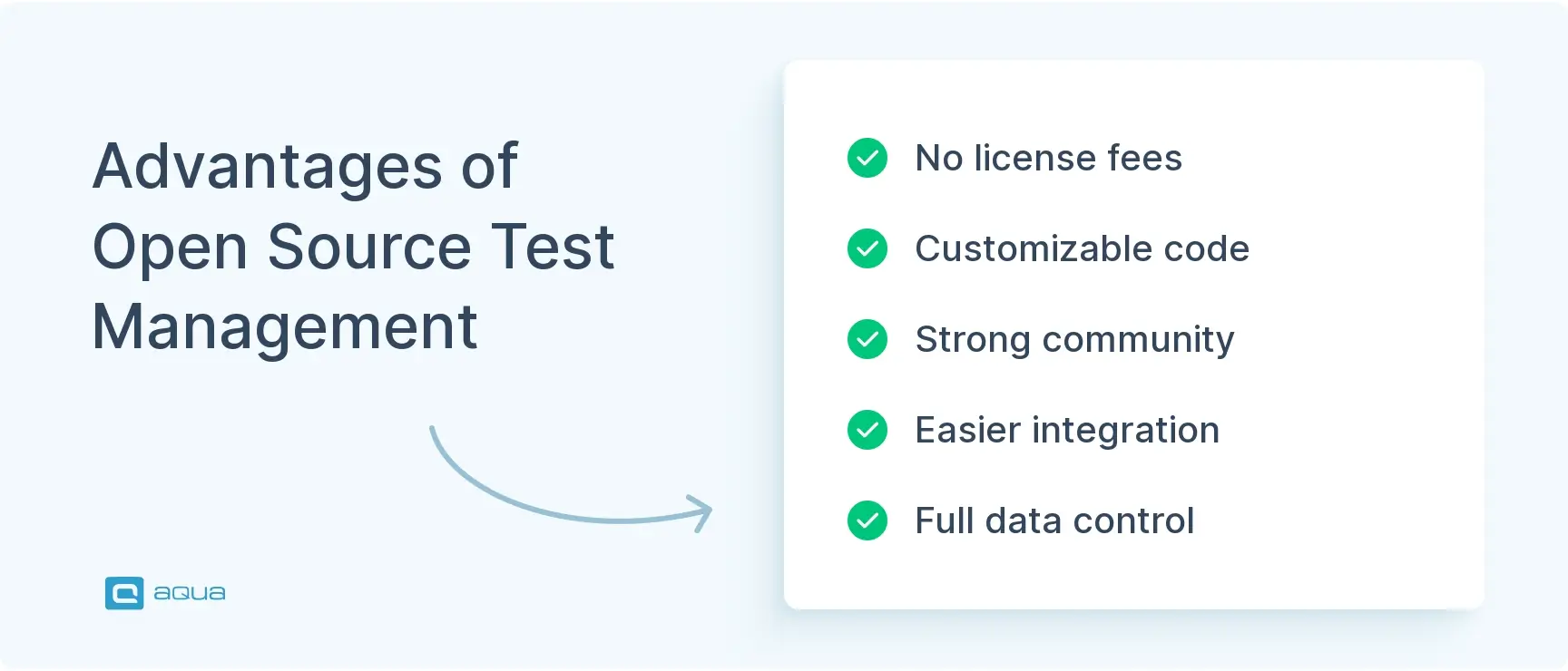
Open source test management tools are software that help QA teams organize, track, and report on their tests while providing access to the source code. These tools run under licenses like GPL, MIT, or Apache. It means you can use, modify, and distribute such software without license fees.
Open source software combines cost efficiency with flexibility. You can download and set them up at a low cost, then customize to match specific workflows or integrate with systems in place. This is most useful for organizations with unique testing processes or those who want to avoid vendor lock-in.
The open source model creates active forums around these tools, where users contribute the following:
- Improvements
- Bug fixes
- Extensions
- Update suggestions
Such community-centered collaboration benefits software progress. After all, new features and integrations are developed by the very people who use that software in their daily routine. If your team is smaller or has a tight budget, this community support can replace dedicated customer service. Though keep in mind that response times are less predictable.
List of 13 best Open Source Test Management Tools
Most QAs would agree that the ideal test management platform should offer test case organization and reporting capabilities. They may also mention that the tool should be reliable, yet have a high-performing UX. The idea here is that the requirements are typically vast, and choosing the solution that meets most of them is no easy task. To assist you, aqua has prepared a list of the best open source test management tools available in 2025. But before you proceed with the review of tools, there’s one more thing.
Your team can greatly benefit from a platform that boosts testing across all QA stages. While open-source solutions can seem attractive at first, many organizations end up covering gaps in reporting and automation with them.
Open source is what many small and medium-sized companies choose as an additional tool in their tech stack. While aqua cloud, an AI-powered test management system, is not open source, it goes far beyond what open-source products can offer. aqua cloud covers all your test management needs at an affordable cost, giving you a comprehensive environment that works straight out of the box. With aqua, you get a dedicated customer success team and top-level support, including consistent updates, SLA-level responses, and predictable release cycles. aqua’s domain-trained AI Copilot creates test cases, test data, and requirements from text documents, voice recordings, images, or your existing documentation. Beyond AI, aqua provides the enterprise-grade reliability most open-source stacks lack, plus deep Jira and CI/CD integrations, flexible dashboards, and a clean, modern interface your team will actually enjoy using.
Obtain an 80% efficiency boost with your testing workflow under one platform
1. Kiwi TCMS
Kiwi TCMS is one of the most active open source test management systems today. Its modern interface and strong features make it the top choice for teams who want a complete test management solution without license costs.
The platform handles test cases in hierarchical structures, test cycle plans, execution tracking, and links to external issue trackers. What separates Kiwi from many other open source alternatives is its active support. Version 15.0 came out in September 2025, and the project keeps moving forward.
Key Features:
- Rich API support for automation integration
- Multiple user roles and permissions
- Test plan management with execution tracking
- Bug tracker integration (Jira, Bugzilla, GitHub)
- Extensive filtering and search capabilities
Pros:
- Active support and frequent updates
- Modern UI that doesn’t feel dated
- Docker containers for easy deployment
- Strong documentation and community support
- Enterprise version available if commercial support is needed
Cons:
- Steeper learning curve than some alternatives
- Less polished than premium commercial options
- Some advanced analytics require additional tools
2. TestLink
TestLink has been around for over a decade in the open source test management space. The interface looks dated next to newer options, but it still provides reliable core functions for test case management and execution.
Many teams like TestLink’s direct approach to test suites, test plans, and result documentation. It’s been on the market a long time, which means there’s a lot of community knowledge and resources for troubleshooting or customization.
Key Features:
- Test case creation and management
- Test plan design and execution tracking
- Requirements specification and coverage analysis
- Basic reporting and metrics
- Integration with bug tracking systems
Pros:
- Stable and proven platform
- Simple to understand and implement
- Large existing user base with abundant resources
- Highly customizable with direct database access
- Lightweight deployment requirements
Cons:
- Dated user interface
- Slower development cycle than newer alternatives
- Limited built-in reporting capabilities
- Less intuitive for new users than modern tools
The best one is obviously testlink, you need to have your own database though. Hosting it in a cloud service will make sure it is accessible and secure.
Split-Opposite
Posted on
Reddit
3. Squash TM
Squash TM takes an open-core approach to test management with a solid free version and optional paid extensions. The platform handles requirements management and test case organization particularly well.
Squash TM has a clean, easy interface with strong traceability features. Teams can map requirements to test cases and track coverage across releases, which makes it valuable for projects with complex compliance needs.
Key Features:
- Requirements management with full traceability
- Campaign planning and execution
- Test automation integration
- Jira connector built-in
- Step-by-step test case design
Pros:
- Polished, modern interface
- Strong requirements mapping capabilities
- Docker images available for quick deployment
- Open-core model with commercial support options
- Active community and regular updates
Cons:
- Some advanced features require paid editions
- Documentation can be sparse in certain areas
- Less extensible than fully open alternatives
4. Allure TestOps
Allure TestOps builds on the popular Allure Report framework to create a full test management solution. The complete product has commercial parts, but the core reporting engine stays open source and works as a strong hub for test results.
Teams that invest in automation note that Allure transforms complex test results into clear reports. Overall, the platform does a great job of providing continuous trend analytics.
Key Features:
- Beautiful, interactive test reports
- Automatic flaky test detection
- Historical trend analysis
- Framework-agnostic result aggregation
- Test case management with manual and automated tests
Pros:
- Outstanding visualization of test results
- Error-free integration with CI/CD pipelines
- Strong support for multiple automation frameworks
- Active support and regular updates
- Growing community of users and contributors
Cons:
- Full test management features require the paid version
- More focused on reporting than test case organization
- Requires additional setup for complete test management
5. ReportPortal
ReportPortal focuses on test execution results rather than test case management. It’s a strong open source analytics platform that uses machine learning to categorize failures, detect patterns, and provide insights into test quality.
For automation-heavy teams, ReportPortal offers a central hub for test results across frameworks and builds. It identifies unique failures versus repeat issues, which makes it valuable for large test suites.
Key Features:
- ML-powered failure analysis and categorization
- Real-time dashboards and reporting
- Integration with major test frameworks
- Historical trend analysis
- Configurable quality gates for CI/CD
Pros:
- Advanced analytics capabilities
- Strong CI/CD integration
- Real-time result processing
- Excellent for managing flaky tests
- Docker-based deployment
Cons:
- Not a complete test case management solution
- Requires pairing with other tools for a full test workflow
- Steeper learning curve for configuration
6. Selenium
Selenium has become the standard for web application test automation. As an open source framework, it lets testers write scripts that control web browsers and simulate user interactions across different browsers and platforms. Selenium’s real strength is its flexibility and wide adoption. It supports multiple languages (Java, Python, C#, Ruby, JavaScript), so teams can write tests in their preferred language.
As a standalone solution, Selenium is primarily a test automation tool and lacks many test management capabilities. But when it comes integrated with leading solutions like aqua, then it fully shines. Another great thing about this solution is that aqua has integration with Selenium, as well as with a range of other useful tools.
Key Features:
- Cross-browser testing (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge)
- Multi-language support for test scripts
- Selenium Grid for parallel test execution
- WebDriver protocol for browser automation
- Integration with major test frameworks (JUnit, TestNG, PyTest)
Pros:
- Industry-standard with a massive community
- Open source with no licensing costs
- Highly flexible and extensible
- Works with all major programming languages
- Excellent integration ecosystem
Cons:
- Requires programming knowledge
- Steep learning curve for beginners
- Test maintenance can be challenging
- No built-in reporting capabilities
- Can be brittle with dynamic web elements
7. SpecFlow
SpecFlow brings behavior-driven development (BDD) to the .NET ecosystem. It lets teams write executable specifications in plain language with the Gherkin syntax. More than that, SpecFlow supports the expression of requirements in a readable format that can be automated.
The framework works smoothly with .NET test runners and CI/CD pipelines. That’s why it’s a natural fit for teams in the Microsoft technology stack. SpecFlow transforms Gherkin scenarios into executable tests that validate application behavior from a user’s perspective.
Key Features:
- Gherkin syntax for readable test specifications
- Native .NET integration with Visual Studio
- Step definition binding to C# code
- Living documentation generation
- Integration with popular test frameworks (NUnit, xUnit, MSTest)
Pros:
- Facilitates collaboration between technical and non-technical stakeholders
- Excellent Visual Studio integration
- Strong support for .NET ecosystem
- Active development and community
- Commercial SpecFlow+ tools available for advanced features
Cons:
- Limited to .NET platforms
- Requires team buy-in to BDD approach
- An additional layer adds complexity
- Step definition maintenance can grow unwieldy
- Learning curve for Gherkin syntax patterns
8. Robot Framework
Robot Framework uses a keyword-driven testing method with a simple, tabular syntax. Tests are readable even for non-programmers, but the framework still provides the power and flexibility for complex automation.
Robot Framework has an extensive library ecosystem. From web automation to API testing, database verification to SSH connections, there’s probably a library for what you need to test. Teams can create custom keywords that hide complexity and promote reuse.
Key Features:
- Keyword-driven test automation approach
- Extensive built-in and external libraries
- Rich ecosystem including SeleniumLibrary for web testing
- HTML test reports with detailed logs
- Support for data-driven testing
Pros:
- Highly readable test cases
- Lower barrier to entry than code-heavy frameworks
- Excellent reporting out of the box
- Platform-agnostic (Windows, Linux, macOS)
- Strong community and library ecosystem
Cons:
- Can feel verbose for simple tests
- Custom keyword management requires discipline
- Less intuitive for developers used to code-first approaches
- Performance overhead compared to pure code frameworks
- Debugging can be more challenging
9. Nitrate
Nitrate came from Red Hat back in 2009 and has been one of the most stable open source test management tools for manual testing ever since. Built with Python and Django, it was designed to replace Testopia and has developed into a full test case management system with strong integration capabilities.
The platform manages test plans, test runs, and test cases with flexibility and power. Nitrate integrates well with bug trackers like Bugzilla and Jira, offers QPID messaging, and provides XML-RPC APIs for automation. For teams that value proven technology over the latest trends, Nitrate delivers reliability without unnecessary complexity.
Key Features:
- Complete test lifecycle management with plans, cases, and runs
- Multiple authentication backends including Bugzilla and Kerberos
- Strong access control for each plan, run, and case
- XML-RPC API with Python client library
- Built-in issue tracker with external integration support
Pros:
- Django-based with straightforward deployment options
- Supports multiple databases: MariaDB, MySQL, and PostgreSQL
- Commercial support available from third-party providers
- Relatively easy to learn with 30-60 minute onboarding
- Well-suited for teams of any size
Cons:
- Development pace is slower than newer alternatives
- Cannot schedule or execute automated scripts directly
- Interface feels dated compared to modern platforms
- Requires Python/Django knowledge for customization
- Smaller community than commercial alternatives
10. Testkube Agent
Testkube Agent is a completely open source test orchestration and execution framework built specifically for Kubernetes-native applications. The agent can run in standalone mode, managed directly through the Testkube CLI or API, making this community-supported alternative free to use without requiring an external control plane.
Unlike cloud-based testing platforms that simulate environments, Testkube is Kubernetes-native and orchestrates tests directly inside your clusters. Tests run as Kubernetes jobs, taking advantage of Kubernetes’ native capabilities for scaling, isolation, and resource management. For teams deep in the Kubernetes ecosystem, Testkube Agent brings testing into their existing infrastructure.
Key Features:
- Test Workflows for managing workflows and templates with execution scheduling
- Webhooks for real-time integration with third-party tools
- Event triggers that automate tests based on Kubernetes events
- REST API for programmatic access to agent features
- Support for multiple test frameworks, including K6, Postman, Cypress, and Playwright
Pros:
- Completely open source with no licensing costs
- Runs tests inside the cluster for better networking security
- Framework-agnostic with support for major testing tools
- Integration with popular CI/CD tools like Jenkins and GitHub Actions
- Can connect to Testkube Control Plane later for enterprise features
Cons:
- Advanced orchestration features like complex test suites and parallel execution require the commercial Control Plane
- Requires Kubernetes cluster infrastructure
- REST API has no authentication by default in standalone mode
- Steeper learning curve for teams not familiar with Kubernetes
- Services and dependency spawning unavailable in standalone mode
11. TestCaseLab Open Source
TestCaseLab offers an open source edition that focuses on direct test case management with a clean, modern interface. The tool balances simplicity and function, offering just enough features without being too much.
Teams like its logical organization of test suites, test cases, and test runs, which makes it easy to structure testing efforts across multiple projects. The platform provides enough flexibility to adapt to different testing methods.
Key Features:
- Hierarchical test case organization
- Test run execution and tracking
- Simple requirements mapping
- Basic reporting and metrics
- User role management
Pros:
- User-friendly interface
- Logical test organization
- Quick to implement and learn
- Regular maintenance updates
- Active user community
Cons:
- Limited advanced features
- Less extensive integrations
- Basic reporting capabilities
- Smaller support compared to leaders
12. Salome-TMF
Salome-TMF (Test Management Framework) offers a thorough approach to test management with a focus on technical testing environments. Originally developed for engineering applications, it provides strong capabilities for complex testing scenarios.
The platform handles test environments, configurations, and detailed test specifications particularly well. Its structured approach makes it valuable for teams with complex testing requirements across multiple configurations.
Key Features:
- Detailed test environment management
- Configuration-aware test execution
- Comprehensive test specifications
- Requirements traceability
- Technical result analysis
Pros:
- Excellent for complex testing environments
- Strong configuration management
- Detailed technical documentation
- Structured approach to testing
- Active in specialized industries
Cons:
- Steeper learning curve
- More technically focused than user-friendly
- Specialized for certain industries
- Less intuitive for simple test cases
- Requires more setup time
13. RedCase
RedCase integrates test management directly into Redmine, the popular open source project management platform. For teams already on Redmine, this plugin provides a smooth way to add test case management without introducing a separate tool.
RedCase uses Redmine’s existing infrastructure, which lets teams link test cases directly to issues, projects, and milestones. This integration creates better traceability between development tasks and testing activities.
Key Features:
- Native Redmine integration
- Test suite organization
- Test execution tracking
- Link tests to Redmine issues
- Redmine’s user management
Pros:
- Error-free Redmine integration
- No additional system to maintain
- Uses familiar Redmine interface
- Direct linking to issues
- Leverages existing Redmine permissions
Cons:
- Requires Redmine instance
- Limited standalone capabilities
- Fewer specialized testing features
- Basic reporting options
- Smaller developer community
I've used Excel spreadsheets before and it was to hard to keep organized (and it was just two of us), and impossible to repeat test cases with. So, I don't recommend using spreadsheets.
Valuable-Ad9157
Posted on
Reddit
Tips for choosing the Best Open Source Test Management solution
Pick the best test management solutions by thinking carefully about your team’s specific needs, technical capabilities, and long-term goals. The perfect solution will integrate with your existing workflows while providing room to grow. Here are essential factors to consider:
First, assess your team’s actual needs rather than being swayed by feature lists. A tool with fewer features that perfectly matches your workflow can be more valuable than a complex solution with capabilities you’ll never use. Consider the types of testing you perform, the size of your test suite, and how you organize your tests.
Your existing technology should heavily influence your decision. Look for tools that integrate well with your current development platforms, issue trackers, and CI/CD pipeline. Native integrations will always be smoother than custom connectors or manual workarounds.
Now, let’s move on to the actual factors for choosing your next open source test management tool:
Key selection criteria:
- Community health: Evaluate the project’s activity level, release frequency, and community size. A tool with regular updates and an active community will continue improving and have better resources available.
- Deployment flexibility: Consider whether you need on-premises hosting for security/compliance or if cloud deployment works for your team.
- Scalability: Will the tool grow with your team? Some solutions work well for small groups but struggle with thousands of test cases.
- Customization potential: Assess how easily you can adapt the tool to your specific workflows and terminology.
- Integration capabilities: Check for native connections to your bug tracker, automation frameworks, and CI/CD tools.
- Learning curve: Consider the training time required for your team to become productive with the new tool.
- Reporting capabilities: Ensure the tool provides the insights you need to track quality metrics and make decisions.
- Security features: Evaluate user management, access controls, and audit capabilities, especially for regulated industries.
Don’t underestimate the importance of user experience. After all, a tool with an intuitive interface will see higher adoption and more consistent use. You may consider arranging a pilot adoption project with actual team members to gauge their response. If successful, you will commit to a full implementation with confidence.
Open Source Test Management Tool Limitations
Open source test management tools offer big advantages in cost and flexibility, but they come with certain limits that teams should understand before they commit. Know these potential drawbacks so you can make an informed decision and prepare strategies to address any gaps.
The most noticeable limitation often lies in the user interface and experience. Many open source vs commercial tools for manual testing lack the polish and intuitive design of their commercial counterparts. This can mean steeper learning curves and lower adoption rates among team members who are used to more refined interfaces. Support represents another significant consideration. Without paid support contracts, you’ll rely on community forums, documentation, and your own technical team to resolve issues.
Here’s a list of feature-related blockers for your consideration:
Common limitations:
- Uneven feature development: Core features may be great while supporting capabilities remain basic or missing entirely.
- Integration challenges: While APIs often exist, pre-built integrations with other tools may be limited or require custom development.
- Security and compliance: Enterprise-grade security features like SSO/SAML, fine-grained permissions, or audit trails may be not available.
- Analytics and reporting: Built-in reporting is typically more basic, often requiring additional tools like Allure Report or ReportPortal for advanced analytics.
- Maintenance burden: Self-hosted solutions require infrastructure maintenance, updates, and security patches.
- Documentation quality: Documentation may be incomplete, outdated, or assume technical knowledge.
- Inconsistent release cycles: Some projects release frequently while others may go months or years between updates.
- Limited scalability: Performance may degrade with very large test suites or many concurrent users.
To handle these limitations, many organizations use a hybrid approach. For instance, use Kiwi TCMS for test management while adding ReportPortal for advanced analytics. This creates a strong combined solution. Others might add targeted commercial products for specific needs, like compliance reports.
Remember that the total cost of ownership includes not just the software, which is in this case free of charge. You also should take into account infrastructure, maintenance, integration, development, and internal support expenses.
Before choosing an open-source test management stack, we advise you to weigh the hidden costs and the time spent on connecting tools that were never built to work together. Over time, these expenses can outweigh the price of a unified commercial solution. aqua cloud offers a smarter path forward. It centralizes every testing asset in one place, giving you end-to-end visibility and effortless traceability. aqua AI Copilot, when trained on your own documentation, helps you generate and maintain test cases that fit your exact project context. At the same time, defects sync with Jira, requirements link to Confluence, and Azure DevOps stays updated due to our native integrations. Selenium scripts, Jenkins pipelines, and Ranorex suites can also be connected to our AI test management solution. With aqua, cutting repetitive work without sacrificing quality is so easy.
Cut testing time by 40% and gain AI-driven clarity at every release.
Conclusion
Open source test management tools have become viable alternatives to commercial solutions over time. Due to that, there’s likely an open source test management tool that fits your team’s specific needs. However, be realistic about the trade-offs. While you’ll gain cost benefits and flexibility, you may need to accept some limitations in user experience or advanced features.