Key takeaways
- SAP ERP testing is critical because system failures can cause complete operational collapse, affecting payroll accuracy and core business operations.
- Effective SAP testing must cover four key areas: customizations with ABAP code, updates and configurations that alter standard processes, integrations with external systems, and data migrations that ensure business continuity.
- Organizations need multiple testing types, including unit testing for code validation, integration testing across modules, functional testing for business processes, performance testing for load handling, and regression testing for change validation.
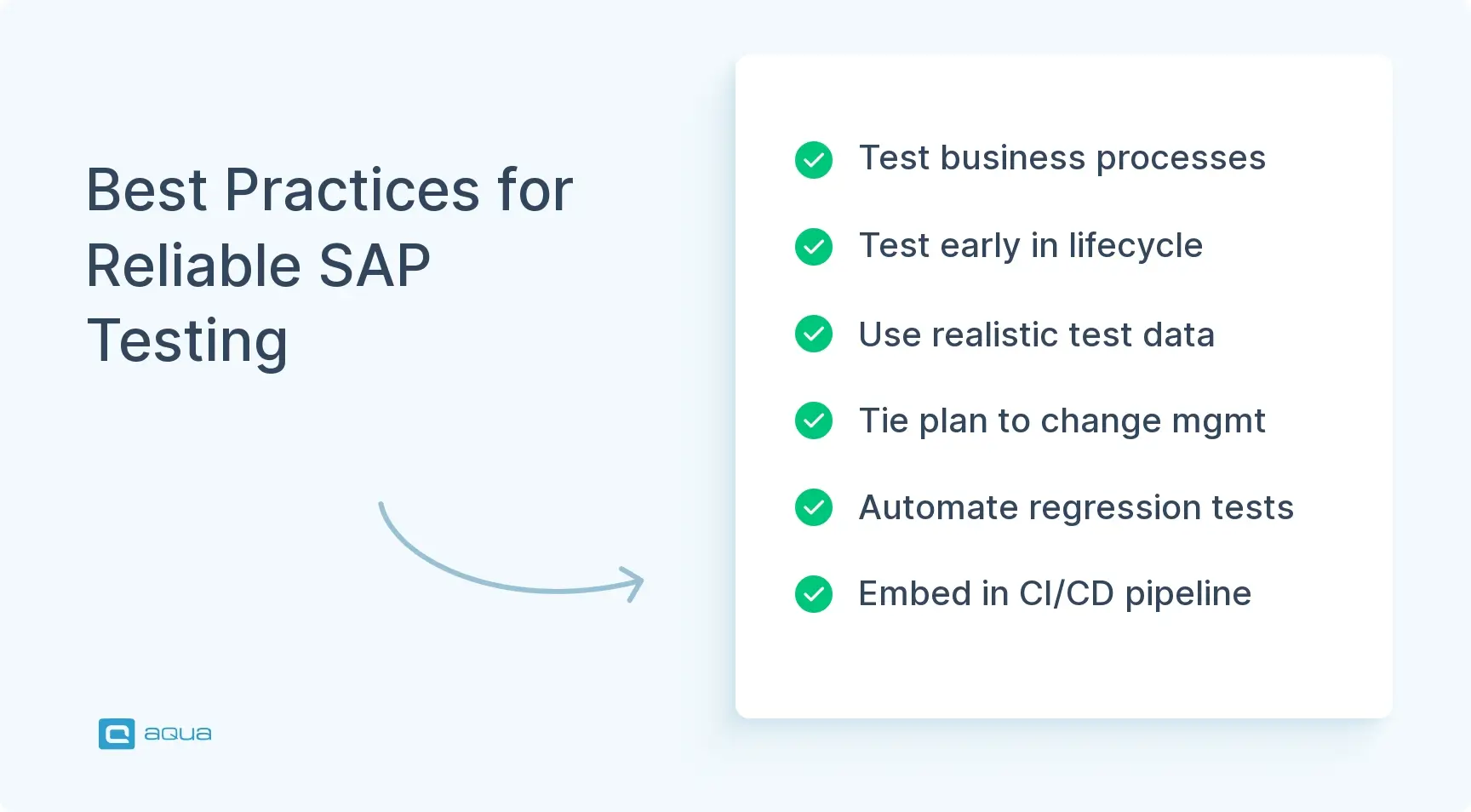
- Best practices include designing tests around business processes rather than modules, testing early in development cycles, and integrating testing into CI/CD pipelines.
Any SAP implementations without proper testing are exposed to catastrophic risks, including operational shutdowns and revenue loss. Learn how to avoid ERP testing failures 👇
Why SAP Testing is Essential for ERP Projects
SAP implementations that skip thorough testing face predictable patterns of failure. Among potential issues are cross-module integration problems between HR and payroll systems that lead to payment errors. As you know, such shutdowns impact employee trust and company credibility. Furthermore, migration from legacy systems without proper validation may create inconsistencies that surface only after go-live. Not to mention exception scenarios like employment changes, special pay adjustments, and backpay calculations often get overlooked during testing. Yet these edge cases cause the most disruption in production.
Timing compounds the risk. If you rush implementations to meet arbitrary deadlines or launch during peak business periods face amplified consequences. So, the pattern is clear. When SAP ERP software testing fails, businesses pay in cash, credibility, and customer confidence. The choice is between investing in thorough testing upfront or paying multiples of that cost in operational damage, emergency fixes, and lost business.
That’s why the importance of SAP testing in ERP projects is basically this framework being a preventive measure. It shields against any negative consequences of dev implementations. Without further ado, let’s review areas of SAP testing of apps.
Key Areas to Test in SAP Applications
SAP testing is centered around the business processes that keep your company up and running. You need to focus on four major segments, each carrying unique risks.
1. Customizations
Every SAP instance has custom ABAP code, enhancements, BAdIs, and user exits tailored to specific business needs. These Z objects aren’t covered by SAP’s standard testing guidance. Common issues include:
- Performance bottlenecks that slow down order processing
- Logic errors that surface only on edge conditions
- Authorization bypasses that create security holes
Thorough unit-testing and integration-testing of custom code is essential before deployment.
2. Updates and configurations
Patches, support packs, and configuration tweaks happen all the time. Any one of them can mess with how your standard SAP processes work. Adjust a pricing condition in SD? You might end up with invoices showing the wrong taxes. Tweak a GL account assignment in MM? Financial postings could land in the wrong accounts. That’s where regression testing comes in. Skip it, and you’ll spend your days chasing down bugs that pop up out of nowhere.
I work in SAP QA. You need a ton of SAP implementation knowledge to make meaningful contributions; otherwise, you'd be stuck automating random tests.
Spirited_Fun9467
Posted in
Reddit
3. Integrations
SAP connects to external systems through IDocs, RFC/BAPI calls, and middleware like PI/PO or CPI. These interfaces are lifelines. When they fail, data doesn’t flow. Typical problems include:
- Silent failures where data gets lost without errors
- Partial transfers that corrupt records
- Mapping errors that scramble fields
Integration testing catches these before they paralyze operations.
4. Migrations
Moving data from legacy systems into SAP or upgrading from ECC to S/4HANA carries substantial risk. You need to validate data integrity, reconcile volumes, and ensure business logic still holds after the move. Companies that build data models on untested assumptions face expensive failures. Custom logic requires validation against real-world scenarios. Data consistency between old and new models must be verified systematically. Migration and reconciliation testing are survival requirements, not optional activities.
When it comes to SAP ERP testing, many companies find themselves caught between high stakes and limited resources. This is where aqua cloud, an AI-powered test and requirement management platform comes in as a solution for complex enterprise systems. With aqua’s AI-powered test case generation capabilities, you can create detailed test scenarios for SAP customizations and integrations in seconds rather than hours. The platform’s domain-trained AI Copilot doesn’t just generate generic tests. It learns from your SAP documentation to create project-specific scenarios that address your unique configurations and business processes. This ensures your testing covers the exact revenue-critical and compliance-sensitive workflows that keep your business running. aqua integrates with Jira, Azure DevOps, GitHub, CI/CD tools, and other solutions to fit directly into your existing workflow.
Achieve 100% SAP test coverage with aqua
Types of SAP ERP Testing
SAP ERP testing requires a portfolio of testing types, each targeting different risks and stages of the development lifecycle.
1. Unit testing
Unit testing focuses on individual ABAP classes, Fiori components, and custom functions. Developers use tools like ABAP Unit and the ABAP Test Cockpit for static checks. This is your first line of defense. If a custom pricing formula or a custom BAdI implementation has a logic flaw, you catch it here before it touches any end-to-end process.
Key characteristics of unit testing:
- Fast and repeatable execution
- Essential for finding bugs early when they’re cheap to fix
- Focused on individual code components
- Runs in isolation without dependencies on other modules
2. Integration testing
Integration testing validates how different SAP modules and external systems work together. For example, an order-to-cash flow touches SD and FI/CO. Sometimes it also involves CRM or e-commerce platforms. Integration tests ensure that when a sales order is created, it triggers the right financial postings and generates accurate billing documents.
Tools like SAP Solution Manager’s Test Suite and Tricentis Tosca are built for this. They let you script or model complex, multi-step flows and verify that data moves correctly across system boundaries. Integration testing catches the failures where everything looks fine but data gets corrupted or lost in transit.
Common integration test scenarios include:
- Order-to-cash flows spanning SD, FI, and warehouse management
- Procure-to-pay cycles connecting MM, FI, and vendor management
- Master data synchronization between SAP and external systems
- Real-time inventory updates across distribution centers
3. Functional testing
Functional testing confirms that SAP processes behave according to business requirements. You’re testing order creation, invoice generation, and payroll calculation. The bread and butter of your operation. Functional tests can be manual or automated. SAP’s eCATT is the legacy approach, but modern teams lean on codeless automation platforms like Panaya or Tricentis. These tools let business users define test cases without scripting, making it easier to maintain test coverage as requirements evolve.
Functional testing typically covers:
- Standard transaction workflows like ME21N for purchase orders
- Custom business process variants specific to your organization
- Exception handling and error scenarios
- User interface behavior and data validation rules
4. Performance testing
Performance testing checks whether your SAP system can handle real-world load without choking. You simulate hundreds or thousands of concurrent users executing transactions like order entry or MRP runs. Then you measure response times, throughput, and system stability. Tools like Tricentis NeoLoad or LoadRunner create the load. Monitoring tools track CPU and memory performance.
If you skip performance testing under peak seasonal load, you discover capacity problems only when business demand is highest. This creates maximum operational and financial damage.
Performance testing focuses on:
- Response times for critical transactions under normal load
- System behavior during peak usage periods
- Database query optimization and bottleneck identification
- Memory consumption and resource utilization patterns
5. Regression testing
Regression testing ensures that existing processes still work after changes like patches or configuration tweaks. SAP systems are constantly evolving, and regression is your safety net. The challenge is scope. You can’t retest everything after every change, so you need a risk-based approach.
Tools like Panaya and Worksoft use impact analysis to identify which processes are affected by a change. They propose a minimal, safe regression suite. Automated regression packs run on a schedule. Nightly, weekly, or triggered by each transport. This catches regressions before they reach production. Without regression testing, you’re deploying changes blind.
Best Practices for Effective SAP Testing in ERP Projects
SAP testing done right is a risk management discipline built into how you operate your ERP. Here are the practices that separate functional teams from those courting disaster.
1. Design around business risk, not modules
Stop thinking in terms of FI, MM, or SD. Start thinking in terms of end-to-end processes like order-to-cash or procure-to-pay. Prioritize based on business impact. If a process touches revenue recognition or compliance obligations, it gets the deepest test coverage. Link every test case to a business owner and a regulatory requirement. Testing then defends specific business outcomes instead of staying abstract.
SAP is very niche, and you can’t jump between regular startup development projects and SAP. If you want to work with SAP, it is a very long road.
2. Shift testing left in the lifecycle
Don’t wait until the end to test. Validate custom designs early with prototype testing and unit tests. Include integration testing in sprints, not only during final system testing. Use static code analysis as part of every transport. Finding defects early is exponentially cheaper than fixing them after go-live. Companies that compress testing timelines to meet arbitrary deadlines accept substantial operational risk.
3. Invest in stable test environments and realistic test data
Maintain at least one production-like environment with representative configuration and data volumes. Use data masking when you copy production data to stay compliant with privacy regulations. Supplement with synthetic test data to cover boundary and exception scenarios. Without good test data, you’re testing fantasy workflows instead of real business operations.
4. Build a master test plan tied to change management
Your master test plan should define scope, milestones, environments, and roles. Include entry and exit criteria. Integrate it with transport management and your release calendar. Companies that fail to align testing with go-live readiness create cutover disasters. A strong master test plan keeps everyone honest about what’s been validated and what’s still at risk.
5. Automate regression and use impact-based selection
Maintain reusable regression packs for each business process. After every change, use impact analysis to reduce test scope intelligently. Tools like Panaya and Worksoft can map changes to affected processes. This lets you run regression frequently without drowning your team in manual test execution. Automation amplifies coverage, but it doesn’t replace business user validation, especially in UAT.
6. Embed SAP testing into CI/CD and DevOps
Integrate your test automation with CI tools like Jenkins or Azure DevOps. Use automated pipelines to spin up test environments and load test data. Run smoke and integration suites. Block promotion to higher systems when tests fail. Continuous testing is the only way to keep up with SAP’s rapid change cycles, especially on S/4HANA Cloud with quarterly innovation releases.
Why SAP Test Automation Is the Optimal Approach
Automation is transforming how teams test SAP. The shift moves from manual, script-heavy approaches to codeless, AI-assisted, continuous testing platforms. SAP systems evolve fast with patches, configuration changes, and quarterly S/4HANA updates. Manual testing simply can’t keep pace. Automation makes testing sustainable and repeatable at scale.
Here’s why modern SAP test automation delivers results:
Codeless test creation
Modern SAP test automation platforms like Tricentis Tosca and Worksoft Certify are built around codeless principles. Business users can define test flows without writing scripts. You model a process like creating a purchase order in MM or receiving goods. The tool translates that into executable tests. When the UI changes, the platform self-heals or prompts a quick fix. You’re not constantly maintaining brittle scripts.
Some benefits of codeless automation include:
- Business analysts can create tests without programming skills
- Faster test creation and maintenance cycles
- Reduced dependency on scarce technical resources
- Self-healing capabilities that adapt to UI changes automatically
AI-driven impact analysis
When you make a configuration change or transport custom code, tools like Panaya analyze your SAP system. They identify affected processes and recommend which test cases to run. This cuts regression scope while maintaining safety. You test what matters, skip what doesn’t, and free up time for exploratory testing and user acceptance testing in SAP.
Continuous testing integration
Continuous testing and orchestration let you integrate SAP test automation into CI/CD pipelines. Worksoft’s Continuous Testing Manager orchestrates regression runs triggered by transports or scheduled nightly. SAP Solution Manager’s Test Automation Framework embeds automation into change cycles. Automated feedback loops catch regressions before they reach production. QA teams don’t need to manually kick off test runs every time something changes.
Data integrity validation
For data-centric testing, platforms like RightData validate data integrity across SAP and analytics stacks. They reconcile extracts, transformations, and loads from SAP BW/4HANA or SAP Datasphere. Tricentis also offers SAP Enterprise Data Integrity Testing for continuous data integrity checks. When your business depends on accurate reporting and analytics, data testing automation protects the pipeline from silent corruption.
Effective SAP testing benefits business continuity and operational excellence a lot. aqua cloud, an AI-driven test and requirement management platform, provides the intelligent testing ecosystem for your business. With its unified repository for all manual and automated test assets, aqua ensures complete traceability from SAP business requirements to test execution and defect resolution. This matters for compliance and audit readiness. The platform’s integration capabilities connect with Jira, databases, and CI/CD tools. This creates a synchronized testing environment across your entire SAP installation. aqua’s AI Copilot with RAG grounding means your test assets stay aligned with your unique SAP implementation. Automation, test case generation, and reporting are always contextually relevant to your business processes. aqua connects with TestRail, Xray, GitHub, Slack, and 10+ other tools you already use.
Save 70% test documentation time with aqua’s AI
Conclusion
SAP runs the operational core of your business. When it fails, revenue stops and compliance breaks. Diligent SAP ERP testing grounded in risk-based planning, end-to-end process validation, and intelligent automation is your safeguard. Major implementation failures are preventable with structured testing, proper environments, and a commitment to validating changes before they hit production. Combine comprehensive testing with best practices and modern automation tools. You’re not just protecting your SAP investment. You’re ensuring operational integrity and business success.