What is AI in Quality Management?
In general, quality management is the continuous process of preventing, finding and fixing issues and keeping all this under control. The end goals of quality management in QA are:
- Delivering a high-quality, reliable product or service
- Meeting user (customer) expectations
- Staying compliant with industry standards
There are two ways you can achieve this:
- Through traditional methods: This way, you rely on human oversight and predefined checklists. Although possible, it gets much more complicated when you have a scalable testing suite.
That’s where inevitable human errors and time-consuming tasks stack up. It’s also why AI usage is necessary.
Example: Quality management in QA spans multiple stages, from test case creation to defect tracking. In software testing, the traditional method of quality management includes going through a lot of test cases by hand or logging defects in a spreadsheet. So much time and energy are lost, but the process is still error-prone. The more the software grows, the number of tests piles up, the harder it gets to keep track of all defects. One defect makes it to production and suddenly costs 100x more.
For years, teams struggled with it. Luckily, you don’t have to do that. Not in 2025. The problems and slowdowns caused by manual efforts created a global necessity for the AI boom we can see in almost every industry. QA is no exception.
- AI-powered quality management: Using artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to speed up and supercharge quality assurance and management.
We will delve into how to use AI to gain full control of your QA without the usual bottlenecks brought by traditional methods. But first, you need to know where AI is used the best in quality management and assurance.
Where Does AI Fit in Quality Management?
Let’s look at some stats showcasing the importance and popularity of AI in QA:
- AI in QA is expected to reach the value of 4 billion dollars by 2026
- 78% of software testers use AI in their efforts
- The market for AI-powered testing tools will reach the value of 2 billion dollars by 2033
So, there is a trend of AI in QA and software testing, and whether you like it or not, you will have to implement it into your processes sooner or later.
However, quality management is a huge process and we need to look at it stage by stage to see where AI is the most efficient.
So, where exactly can AI help, and where does it still need your expertise?
-
Test Planning & Requirement Analysis: Smarter from the Start
Every QA process starts with planning. You gather requirements, define testing scope, and create strategies. Sounds simple, right? Except it’s not.
Common requirements management problems:
- Requirements are often vague.
- Teams can miss critical test scenarios.
- Incomplete documentation leads to bugs that never should’ve existed in the first place.
🤖 How AI Helps: AI can analyse past projects and detect missing details in requirements. Some solutions take it one step ahead – you can even generate these requirements based on a short note, voice prompt, or an image. So AI starts optimising before the testing cycle begins.
You can use:
- ChatGPT or Gemini for requirements analysis, as these AI tools can turn the stakeholder input into requirements and detect the gaps in the existing ones.
- Aqua cloud for requirements generation and traceability, as this solution can turn any type of input into a complete requirement. You can quickly generate PRDs, User Stories, or BDDs by just saying a few words. Good news: you can try this now.
Turn any type of input into a complete requirement with a click
🔹 Example: Imagine you’re testing a new mobile banking app. AI scans the requirements and notices that the document never mentions failed login attempts. Should there be a lockout after five failed tries? AI flags this, prompting the team to clarify.
❌ Where AI Struggles: AI is great at detecting gaps, but it doesn’t understand business logic as humans do. If a requirement is vague but technically correct, AI won’t question it. That’s still a human’s job.
2. AI Boost in Test Case Design & Test Data Preparation
Once the requirements are set, you need test cases. But writing them manually? That’s where things slow down.
- Large applications need hundreds or thousands of test cases.
- Test data needs to be diverse and compliant (especially with GDPR and similar laws).
- Repetitive test case creation eats up valuable time.
🤖 How AI Helps: AI can auto-generate test cases based on requirements, system behaviour and historical defects. It can also create synthetic test data that mimics real-world conditions without privacy risks.
You can use:
- GPT solutions for both test case and test data creation, but as these tools are not specialised in QA, you need a lot of prompting to get the quality you want.
- Tonic.ai for synthetic test data creation.
Or you can go for a dedicated solution like aqua cloud, which does both for you. You can auto-generate test cases from requirements with just one click, and link each test case to its requirement effortlessly for complete coverage. Compared to manual test case creation, it is 98% faster and time-efficient. Aqua cloud also generates thousands of rows of test data within seconds, eliminating privacy and security concerns. The whole process takes just 2 clicks and a few seconds of your time.
Generate test cases and test data in a matter of seconds in 2 clicks with AI
🔹 Example: Let’s say you’re testing an airline booking system. AI can help you generate realistic test data: names, credit card details, flight routes, and even edge cases like “What happens if two people book the last seat at the same time?”
❌ Where AI Struggles: AI-generated tests are efficient but lack creativity. It won’t come up with crazy real-world scenarios (which happen from time to time), like “What happens if a user buys a ticket, cancels it, then immediately tries to rebook with the same points?” So some human input is still needed here.
3. Test Execution & Defect Management: AI Predicts Failures Before They Happen
Once test cases are ready, it’s time to execute them. But running thousands of tests takes forever—and analysing failures is even worse.
💡 Common Problems:
- Flaky tests: A test that fails randomly with no clear cause.
- Redundant execution: Running the same tests even when they aren’t needed.
- Defect triaging: Digging through test logs, guessing if it’s a real bug or just an environment issue.
🤖 How AI Helps: AI predicts which tests are likely to fail and skip unnecessary ones. It also groups similar defects together, making bug reports clearer and faster to analyse.
You can use several tools for this:
- Launchable – Runs only the most relevant tests based on code changes and past failures.
- Testim – Auto-heals flaky tests and detects failure patterns.
- Applitools Test Cloud – Uses visual AI to spot UI defects and group similar bugs.
🔹 Example: Your CI/CD pipeline runs 10,000 tests every night. Instead of blindly executing them all, AI learns from past failures and saves you a massive amount of time by only running the critical 2,000. When bugs appear, AI checks if similar defects already exist, and reduces duplicate tickets.
❌ Where AI Struggles: AI can suggest which tests to run, but it can’t understand new feature risks. If a new payment method was just added, a human still needs to decide if extra tests are needed.
4. Test Automation & CI/CD Integration: No More Flaky Tests
If you automate tests, you know the pain: flaky tests. They can:
- Break pipelines
- Slow down releases
- Cause endless frustration
The Usual Pain Points:
- UI tests fail because of small changes (e.g., a button moves 10 pixels).
- Automation scripts break too easily.
- CI/CD pipelines waste resources running irrelevant tests.
🤖 How AI Helps: AI-powered self-healing automation adapts tests to UI changes. It also prioritises which tests should run in CI/CD, making execution 50% faster.
Available tools for this:
- Testim – Self-healing automation adjusts tests when UI elements shift.
- Mabl – AI-driven test automation detects changes and auto-updates tests.
- Launchable – Selects only the most relevant tests to run, cutting execution time.
🔹 Example: You update your web app, and a button moves slightly. Instead of failing, AI recognises the change and updates the locator automatically. No manual fixing is needed.
❌ Where AI Struggles: AI can adjust selectors, but it doesn’t know why a test exists. If the test logic needs changing (not just UI elements), a human tester is still required.
5. Performance & Security Testing: AI Detects Anomalies Before Users Do
Performance bottlenecks and security vulnerabilities can kill your product. But manual testing often misses hidden issues.
Common Challenges:
- Performance tests only run before major releases, not continuously.
- Security scans detect too many false positives and make it hard to find real threats.
🤖 How AI Helps: AI-driven performance testing detects slowdowns automatically. AI security tools also identify real threats, reducing noise from false alarms.
Tools you can use:
- Dynatrace – AI-powered performance monitoring automatically spots slowdowns.
- Datadog APM – Uses AI to detect anomalies in application performance.
- Darktrace – AI-driven security tool that finds real threats and reduces false positives.
🔹 Example: AI monitors your web app and notices that response times jump by 30% when more than 1,000 users log in. It flags this BEFORE customers complain.
🚨 Where AI Struggles: AI is great at detecting known threats but fails against unknown (zero-day) attacks. A security team is still crucial.
6. Analysis & Continuous Improvement: AI Learns from Your Past Failures
Quality doesn’t stop after release. Production bugs still happen—the key is catching them fast.
The Problem:
- Too many logs. Finding real issues is like a never-ending process.
- By the time you notice a bug, customers are already complaining.
🤖 How AI Helps: AI fully scans logs to detect anomalies and then it alerts teams before things break.
Great examples of these tools:
- New Relic – AI-powered observability tool that detects unusual patterns in logs.
- Splunk – AI-driven log monitoring that predicts system failures.
- Sentry – AI-powered solution that detects app crashes and provides debugging insights.
🔹 Example: Your app crashes randomly once every 10,000 requests. AI detects this pattern before users report it and suggests a fix before your reputation suffers.
🔻 Where AI Struggles: AI can flag problems, but it can’t solve them alone. A team still needs to investigate and deploy fixes.
As you can see, AI comes in handy in a lot of scenarios, but also poses some challenges. Let’s look at them in more detail.
Challenges of Implementing AI in Software Testing
AI brings efficiency and intelligence to QA, this is clear. However, integrating it into your existing workflows isn’t always smooth. Teams face obstacles ranging from tool compatibility to trust in AI-driven decisions.
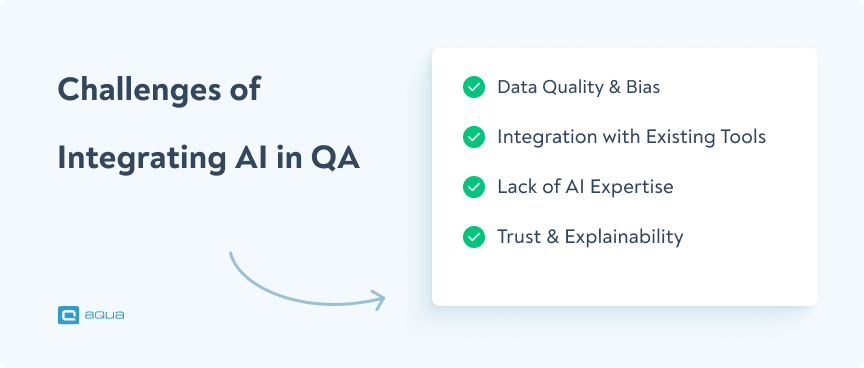
The key challenges of implementing AI in QA:
🔹 Data Quality & Bias: AI relies on data. However, if the training data is flawed or incomplete, the results AI gives will be inaccurate.
Example: Imagine you’re training an AI model to identify bugs in your application. The AI has been fed historical test data, but there’s a problem. Most of that data comes from only one type of project, say, e-commerce websites. Now, when you test a financial application, the AI will struggle to detect security flaws because it was never exposed to similar cases. If your training data is flawed or incomplete, AI’s predictions will be unreliable, leading to missed defects. 60% of AI projects fail exactly for this reason.
🔹 Integration with Existing Tools: Many teams use legacy systems that don’t easily support AI-driven automation, requiring extra effort for compatibility.
Example: You’ve just convinced your team to try AI-driven test automation. The excitement fades quickly when you realise your legacy test management system doesn’t support AI-based reporting. Now you’re stuck manually transferring data between tools or finding workarounds. AI is powerful, but if it doesn’t integrate with your existing ecosystem, it will create more headaches than solutions.
🔹 Lack of AI Expertise: Testers and QA engineers sometimes do not have the expertise to fine-tune AI models or interpret AI-generated results.
Example: Your AI tool just flagged several potential issues in your application. Great! But you and your team aren’t quite sure why it flagged them or how to interpret the risk level. Should you escalate them as critical bugs or dismiss them as false positives? Without solid expertise, you will second-guess its insights or fail to use them effectively.
🔹 Trust & Explainability: Depending on the industry, trust levels in AI can vary. But overall, 3 people in 5 have trust issues with the AI results. In software testing, AI can flag test failures, but if teams don’t trust it, they will hesitate to act on its insights.
Example: Your AI tool just recommended skipping 20% of your regression tests because it “predicts” those areas are stable. Sounds efficient, but how does it know? What if it’s wrong? Without an explanation of the AI’s logic, you will hesitate to trust its recommendations and end up running all the tests anyway. So, AI is only useful when teams can understand how it works and trust its decisions—otherwise, they will ignore its insights altogether.
What you need to do to deal with these challenges:
- Improve data quality and minimise bias by training AI with diverse, real-world test cases.
- Use AI-compatible tools that integrate with your existing test management system.
- Train your QA team to understand and interpret AI-generated results.
- Choose an explainable AI that provides clear reasoning behind its decisions.
Balance AI with manual review for critical testing decisions to remain reliable.
Conclusion
AI in QA is powerful, but it’s not a magic fix. Poor data, tool incompatibility, and lack of expertise will turn AI into a liability instead of an advantage. The key is to use AI wisely. You should train AI with quality data, integrate it properly, and ensure your team understands its insights. When you achieve this, you can easily apply AI in different stages of QA, including requirements analysis, test case and test data generation, CI/CD, and much more. Then AI will make your entire QA process smarter and more reliable.